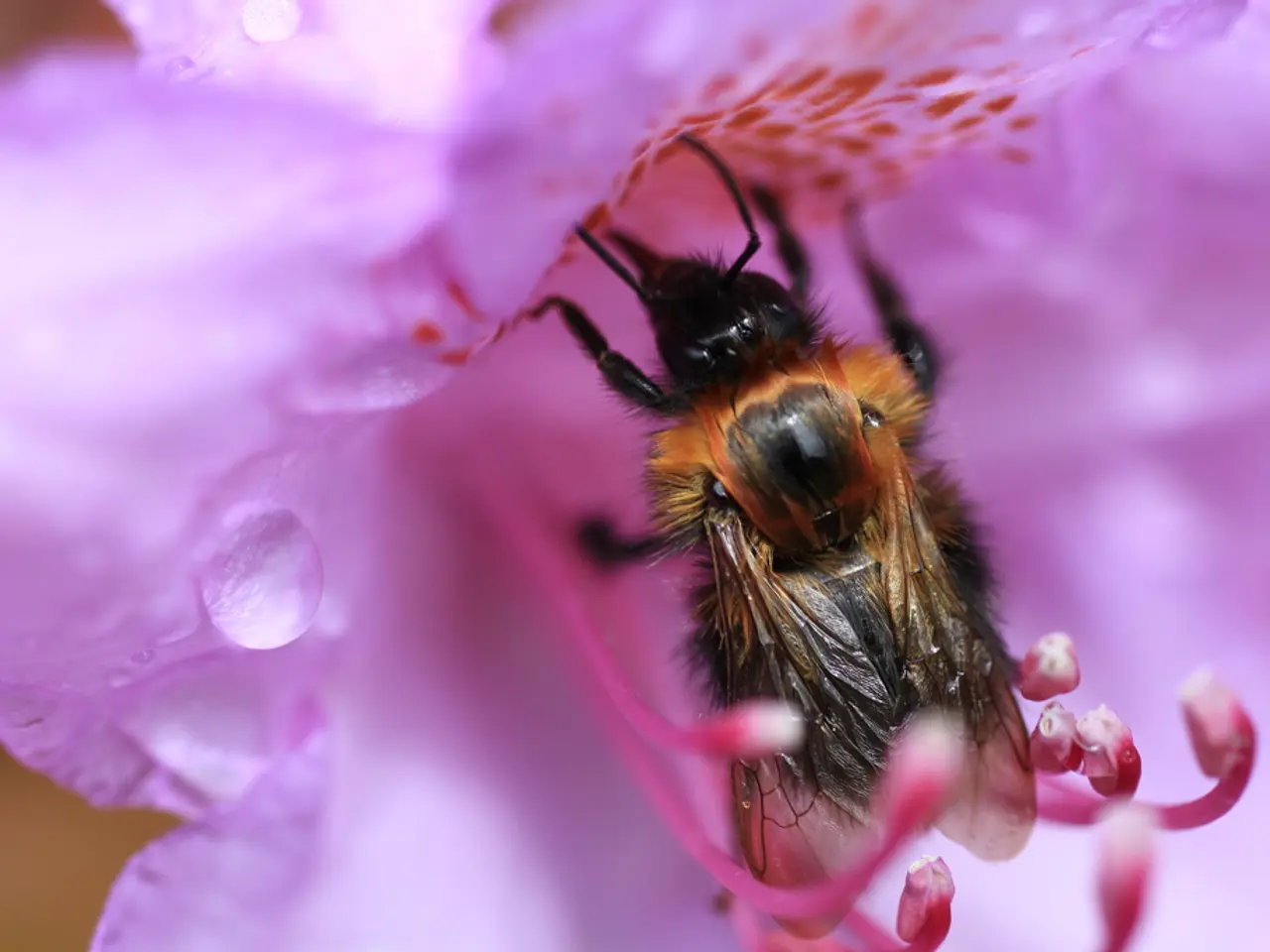
Bees produce a unique type of honey, known as 'Mad Honey', from gathering a particular nectar.
In the heart of remote mountainous regions, a unique type of honey known as mad honey is produced. This honey, with its neurotoxic properties, has a long and intriguing history, having been used both as a weapon and a medicine.
A Historical Weapon and Medicine
Mad honey, containing natural neurotoxins called grayanotoxins, is produced when bees collect nectar from certain plants like Rhododendron species. In 67 BC, Mithridates, the "Poison King," used mad honey from the Caucasus region as a poison to incapacitate Roman soldiers by contaminating their food or drink. This disoriented and sickened the enemies, aiding military victories.
Indigenous groups such as the Gurung people in Nepal have used mad honey in traditional healing and spiritual rituals, believing it to provide vitality and aid in spiritual journeys.
Modern Uses and Production
Today, mad honey is still employed medicinally in some regions like Turkey and Nepal to treat conditions like arthritis, hypertension, and stomach ailments. It serves as a cultural and economic resource for rural communities through traditional harvesting.
Mad honey is produced primarily when honey bees forage on nectar from plants containing grayanotoxins, notably Rhododendron species. The giant Himalayan honey bee, found in Nepal, is notable for producing mad honey due to its preference for rhododendron nectar. Similar processes occur in Turkey's Black Sea region.
Traditional harvesting methods are used in remote mountainous regions, often involving wild collection from cliffs or tree hives. On a scientific level, analysis involves melissopalynological studies (examining pollen types) and extraction with ethanol for further biochemical evaluations.
Risks and Toxicity
Despite its medicinal uses, mad honey carries health risks due to its toxicity. The grayanotoxins in mad honey affect the central nervous system, potentially causing honey intoxication with symptoms like dizziness, nausea, vomiting, hallucinations, low blood pressure, and heart rhythm abnormalities.
Toxic effects come from grayanotoxins that bind to sodium channels in cell membranes, disrupting nerve and muscle function. While moderate use can be medicinal, ingestion of large quantities or unregulated consumption is hazardous and can lead to poisoning.
Modern awareness has lessened accidental poisonings, but cases still occur primarily in regions where the honey is popular or used traditionally. Consuming mad honey can lead to rhythm disorders in the heart, such as bundle branch block.
To mitigate the risk of overdose and poisoning, it's essential to start with small amounts and buy mad honey from reputable sources or trusted local honey hunters. It's also crucial to be aware of the potential risks associated with this unique honey.
In summary, mad honey's uniqueness lies in its neurotoxic properties derived from specific plant nectars, giving it a long history as both a tool of war and traditional medicine. Its production is ecological and region-specific, and its consumption entails risks that must be carefully managed.
- Science has unveiled the nature of mad honey, a unique type of honey produced by certain plants like Rhododendron species, containing natural neurotoxins called grayanotoxins.
- In ancient times, Mithridates, also known as the "Poison King," utilized mad honey as a weapon by contaminating food and drink of his enemies.
- The Gurung people in Nepal have traditionally used mad honey for healing purposes and spiritual rituals, believing it boosts vitality and aids spiritual journeys.
- Today, mad honey is still employed medicinally in regions like Turkey and Nepal for treating various health conditions, including arthritis and hypertension.
- The giant Himalayan honey bee, native to Nepal, is renowned for producing mad honey due to its preference for rhododendron nectar.
- Similarly, mad honey production happens in Turkey's Black Sea region with traditional harvesting methods being employed.
- Analysis of mad honey involves melissopalynological studies and extraction with ethanol for biochemical evaluations.
- Despite its medicinal uses, mad honey can pose health risks due to its toxicity, causing honey intoxication with symptoms like dizziness, nausea, and heart rhythm abnormalities.
- Grayanotoxins, present in mad honey, disrupt nerve and muscle function by binding to sodium channels in cell membranes.
- While moderate use can have medicinal benefits, unregulated consumption remains hazardous and can lead to poisoning.
- Awareness of mad honey's potential risks has decreased accidental poisonings, but cases still occur in regions where the honey is popular or traditionally consumed.
- Consuming mad honey can lead to rhythm disorders in the heart, such as bundle branch block.
- To avoid overdose and poisoning, it is crucial to start with small amounts, buy mad honey from reputable sources, or trusted local honey hunters, and be aware of associated risks.
- Mad honey's history spans both as a tool of war and traditional medicine, due to its neurotoxic properties.
- Production methods involve ecological processes and are region-specific, contributing to rural communities' cultural and economic resources.
- Larger quantities or unregulated consumption can be lethal, necessitating careful management of this unique honey.
- The science behind mad honey continues to intrigue researchers, expanding our understanding of plants, bees, and neurotoxins.
- The environmental impact of mad honey production, particularly its effect on the Rhododendron species' populations, remains a subject of study.
- Modern technology is aiding the analysis and understanding of mad honey's properties, contributing to the field of environmental science.
- The rising interest in health-and-wellness, food-and-drink, and personal-growth sectors has renewed curiosity about unique products like mad honey.
- The finance industry is increasingly focusing on investing in niche products such as mad honey, viewing it as a high-yield, untapped market.
- Personal-finance blogs and articles discuss the potential lucrative also high-risk nature of investing in such products.
- Mainstream media outlets cover stories about the exploits of business ventures specialized in producing, trading, and marketing mad honey.
- Cooking shows occasionally feature mad honey in unique recipes, showcasing its potential use in food and drink.
- The cultural allure of mad honey has found its way into pop-culture, with it making appearances in books, movies, and songs.
- Science fiction and fantasy stories, in particular, frequently feature mad honey for its exotic and dangerous qualities.
- The risks associated with mad honey also extend to the entertainment industry, with concerns over responsible gambling and addiction.
- The gambling trends pillar of general news outlets sometimes covers incidents related to the excessive consumption and poisonings caused by mad honey in casinos and gambling circles.
- Casinos and gambling venues have been identified as hotspots for mad honey poisonings due to its perceived exotic and high-status nature.
- The entertainment sector's role in spreading knowledge about responsible gambling and promoting awareness of mad honey's potential health risks is deemed crucial.
- Cultural festivals have incorporated mad honey as a unique showcase, exposing visitors to its history, production, and risks.
- The first-aid industry is expanding its knowledge on mad honey poisonings, aiding in the development of more effective treatments in tandem with therapies-and-treatments research.
- In football, the Champions League, NFL, WNBA, Baseball, Hockey, Golf, European Leagues, Basketball, NCAA Basketball, MLB, NHL, Premier League, American Football, NBA, Masters, Laliga, NCAA Football, and Tennis, individual athletes and teams have employed various forms of mental-health therapy.
- The growth of therapies-and-treatments in sports reflects an increasing awareness of the importance of mental health in achieving big-wins and career-development.
- The sports industry's efforts in combating gambling addictions, particularly in sports like casino-games, lotteries, and gambling-trends, are crucial for the overall well-being of athletes and fans alike.
- The revival of traditional skills training and education-and-self-development programs focuses on preserving the art of mad honey production and consumption, fostering personal growth and cultural heritage.